Alarming Yellow Fever Outbreaks Grip African Region
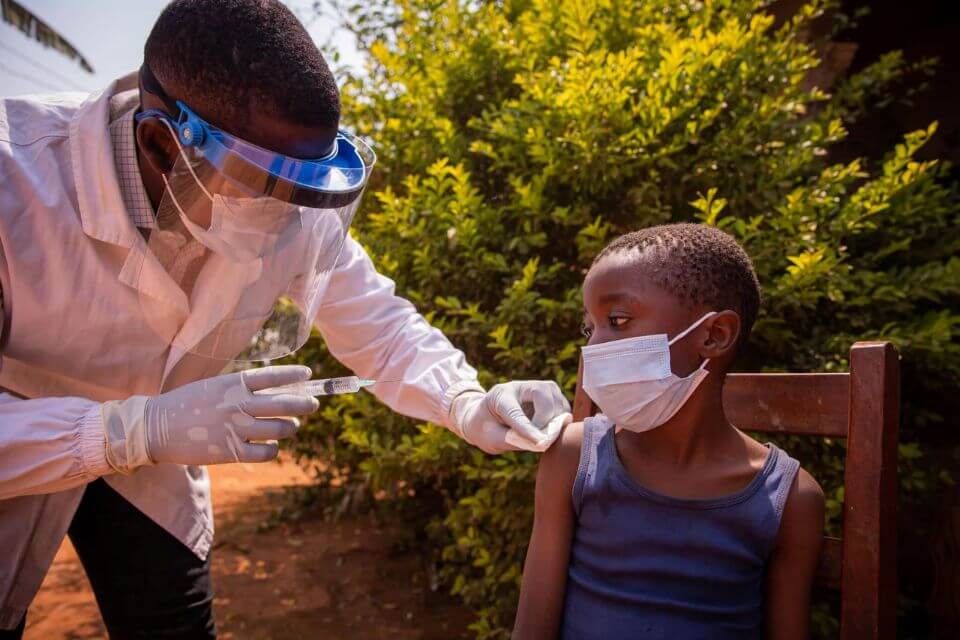
The ongoing yellow fever outbreaks across multiple countries in the African region are raising grave concerns within the global public health community. Since early 2023 through February 2024, a total of 13 nations including Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Chad, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo have reported probable and confirmed cases of this life-threatening viral disease. Preliminary data indicates a staggering 11% case fatality rate in 2023 alone.
As of late 2023 and early 2024, eight of these countries are still battling active yellow fever transmission, with recently confirmed cases emerging in urban centers like Douala in Cameroon. The potential for rapid spread in densely populated cities is particularly alarming. The situation demands an urgent, well-coordinated response to curb rising infections and prevent a worsening regional crisis.
The World Health Organization and affected nations have implemented a range of public health measures, including enhancing disease surveillance, improving laboratory testing capacity, and embarking on extensive vaccination campaigns that reached approximately 62 million people in 2023. Efforts are also underway to strengthen case management, vector control, and risk communication strategies. However, persistent challenges like immunity gaps, surveillance limitations, response delays, and the strain of simultaneous outbreaks continue to hinder progress.
The regional risk level has been re-assessed as moderate by WHO due to the multitude of ongoing outbreaks, potential cross-border spread, and urban transmission risks. While the global risk remains low for now, the situation demands sustained vigilance and coordinated action to prevent a broader international crisis.
WHO is emphasizing active surveillance, prioritizing vaccination, vector control, clear travel advisories, and open information sharing among member states. The global health body stresses there is no justification for imposing trade or travel restrictions, but rather a concerted focus on prevention through public awareness.
The resurgence of yellow fever outbreaks, a disease for which an effective vaccine exists, is highly concerning. It reflects deeper vulnerabilities and health system gaps that must be addressed urgently. As the human costs mount, the international community must lend its full support to control these preventable tragedies and bolster epidemic preparedness in at-risk regions.
Click to View → Mantacc Swab-based Specimen Collection