How Do Saliva Collection Kits Improve DNA Quality and Stability?
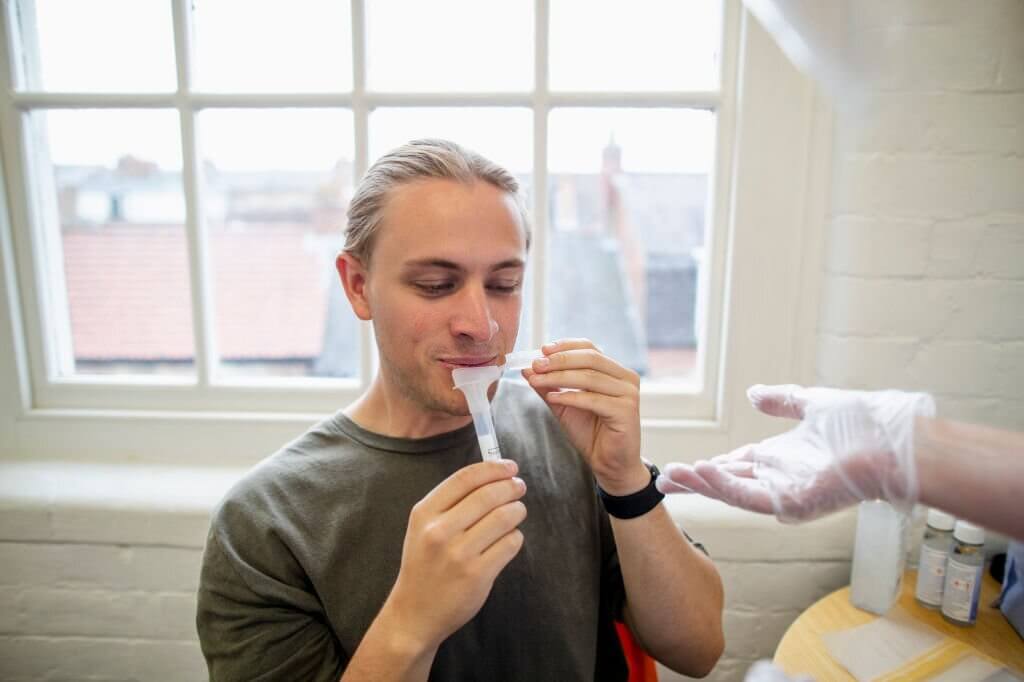

Saliva collection kits are transforming genetic and epidemiological research through non-invasive, mail-based DNA sampling. This article examines how Oragene kits compare to other methods like buccal swabs across key metrics including DNA yield, quality, stability and ease of use.
What are Saliva Collection Kits and Why Use Them?
Saliva collection kits are devices designed to easily and non-invasively collect saliva samples for DNA analysis. They have become increasingly popular for large epidemiological studies because they offer several advantages over traditional blood collection. Saliva collection is simple, painless, and does not require trained staff, allowing samples to be easily collected from large populations or mailed back by participants. The non-invasive nature also improves compliance and follow-up rates compared to blood draws. Saliva contains various biomarkers and cells that allow assessment of DNA quality and yield for genotyping and other genetic analyses. Overall, saliva collection kits simplify logistics and expand possibilities for genetic research.
How Do Saliva Collection Methods Compare for DNA Yield?
A key consideration is how well different collection methods and kits perform for downstream DNA analysis. Studies have compared yields from the Oragene saliva kit to other non-invasive techniques like buccal swabs, cytobrushes, oral rinse, and passive drool. The Oragene kit consistently provides the highest total DNA yields, with medians around 110-180 μg per sample, 3-12 times higher than other methods. For example, in one crossover study of 17 adults, Oragene saliva had a median yield of 181 μg compared to 36 μg for oral rinse and 10-13 μg for swabs and brushes. The high Oragene yield is attributed to its stabilization buffer that lyses cells and prevents degradation. Oral rinse and drool also perform reasonably well. However, cytobrushes and buccal swabs often provide inadequate DNA for applications like microsatellite genotyping, requiring multiple swabs per subject. Overall, Oragene saliva and oral rinse give the highest and most consistent DNA yields.
What About DNA Quality from Different Collection Methods?
Beyond total yield, DNA quality is critical for genotyping accuracy. Important metrics are purity ratios like A260/280 and A260/230, PCR success rate, and integrity on gel electrophoresis. Again, Oragene saliva and oral rinse provide the best results, with A260/280 ratios in the ideal 1.7-1.8 range indicating low protein contamination. Buccal swabs and brushes perform more poorly, with much lower purity ratios showing contamination. PCR amplification rates were 99% for Oragene saliva and 98% for oral rinse, significantly higher than 75-84% for cytobrushes and swabs which had trouble with longer amplicons. The Oragene stabilization reagent appears key to maintaining DNA integrity and purity at room temperature. For both yield and quality, Oragene saliva and oral rinse are preferable to buccal swabs.
How Does Sample Collection Method Affect Salivary Flow Rate?
An important variable is how collection method affects salivary flow rate and total protein levels, which can influence analyte concentrations. Passive drool and swabs give the lowest unstimulated flow rates around 0.5 mL/min. Mechanically stimulated flow is higher at 1-1.5 mL/min for swabs and brushes. Oragene's citrate buffer gives the highest flow rates around 2.5 mL/min due to its acidic pH. Total protein levels don't vary significantly between methods except Oragene has lower levels, likely because of its high flow diluting proteins. Researchers should standardize collection based on desired flow rates and analyte concentrations.
How Well Does Oragene Saliva Withstand Room Temperature Storage?
A key practical advantage of Oragene saliva is its stability at room temperature for extended periods, owing to its biostabilizing buffer. Studies found no decrease in DNA yields or quality in Oragene samples stored up to 8 months at room temperature. A260/280 purity ratios remained ideal, and PCR amplification rates were 98-99% even after 8 months at room temp. This contrasts with oral rinse DNA degrading after 10 days unpreserved. Oragene's stabilitysimplifies sample collection, storage and shipping for large remote studies. However, freezing may still be needed for storage beyond a year to prevent desiccation. Overall, Oragene's buffer preserves DNA yield and quality at room temperature for at least 8 months.
What Are Some Limitations of Saliva Collection Methods?
While saliva collection has many advantages, there are some limitations to consider. Quantification methods like UV spectrophotometry don't discriminate human from non-human DNA from microbes and food debris. Saliva yields also vary with age, sex, hydration status and other factors. Diurnal variations in salivary analytes haven't been well characterized. Finally, on-site versus at-home sampling could produce different participation and return rates, important for feasibility. More research on these parameters will optimize protocols for large epidemiologic biobanking studies.
In summary, saliva collection kits provide a non-invasive approach to obtain high quality DNA for genotyping and biobanking research. Saliva collectionexpand possibilities for genetic epidemiology compared to blood draws. Oragene kits perform well across key metrics of yield, purity, stability and ease of use. Oral rinse also performs adequately but buccal swabs and brushes have limitations. Standardizing and optimizing collection methods is critical to maximize DNA quality and participant rates for population genomics.
Click to View → Mantacc Saliva Collection Kits
References
-
Rogers NL, Cole SA, Lan HC, Crossa A, Demerath EW. New saliva DNA collection method compared to buccal cell collection techniques for epidemiological studies. Am J Hum Biol. 2007 May-Jun;19(3):319-26. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.20586. PMID: 17421001; PMCID: PMC2797479.
-
Nunes AP, Oliveira IO, Santos BR, Millech C, Silva LP, González DA, Hallal PC, Menezes AM, Araújo CL, Barros FC. Quality of DNA extracted from saliva samples collected with the Oragene™ DNA self-collection kit. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012 May 4;12:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-65. PMID: 22559914; PMCID: PMC3422993.
-
Topkas E, Keith P, Dimeski G, Cooper-White J, Punyadeera C. Evaluation of saliva collection devices for the analysis of proteins. Clin Chim Acta. 2012 Jul 11;413(13-14):1066-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.02.020. Epub 2012 Mar 3. PMID: 22405932.
Related Posts
Saliva Collector Benefits for Roadside Drug Testing
Everything You Need To Know About Saliva Collectors
Saliva Collection Kits: The Non-Invasive and Reliable Way to Collect Samples
Saliva Collection Kits: A Versatile Tool for Diagnostics & Forensics