Which Preoperative Swab is Best For Reducing Surgical Site Infections?
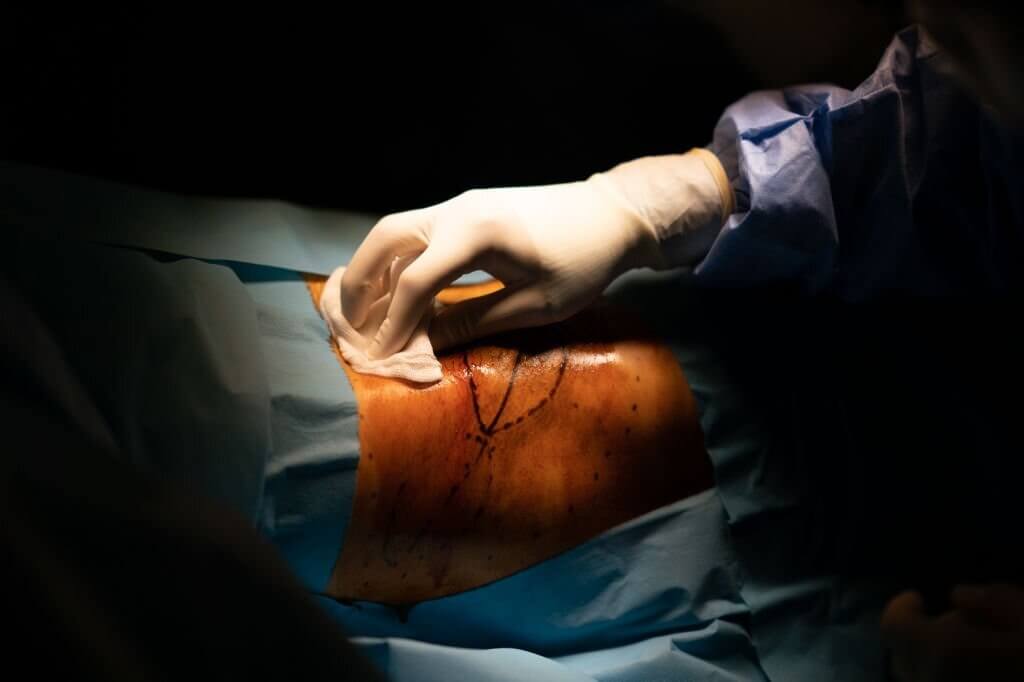
What is the purpose of preoperative skin preparation?
Preoperative skin preparation is an important part of the effort to prevent surgical site infections (SSIs). The skin at the surgical site is cleansed before surgery to remove microorganisms that could lead to postoperative infections. Effective skin antisepsis immediately before incision is a recommended guideline for SSI prevention.
What solutions are commonly used?
Several skin disinfectant solutions are approved for preoperative use. Povidone-iodine, chlorhexidine, and iodine povacrylex in isopropyl alcohol are three common options. Povidone-iodine is an iodophor solution that has been widely used as a pre-surgical scrub. Chlorhexidine gluconate is another antiseptic agent that has demonstrated broad antibacterial activity. Iodine povacrylex provides iodine in a film-forming solution with prolonged activity.
How do the different solutions compare in reducing SSI risk?
Recent studies have compared the efficacy of different skin preparation solutions in reducing postoperative wound infections. A prospective study by Swenson et al. implemented three preoperative skin protocols sequentially in a single center. Patients undergoing general surgery procedures were prepared with either povidone-iodine, chlorhexidine, or iodine povacrylex. The study found significantly lower SSI rates with the use of iodophor-based solutions. The povidone-iodine and iodine povacrylex groups had reduced overall and superficial SSIs compared to the chlorhexidine group.
What patient factors influence SSI risk?
Certain patient characteristics have been associated with higher SSI risk. Female gender, diabetes, cancer diagnosis, sepsis, preoperative weight loss, and longer operative times were identified as factors linked to greater incidence of surgical site infections. The type of surgical wound also impacts infection risk, with clean-contaminated and contaminated wounds having higher rates of SSI compared to clean wounds.
What are the implications for surgical skin preparation?
The choice of skin antiseptic solution appears to influence the likelihood of postoperative wound infections. While chlorhexidine has demonstrated efficacy for central line insertion, iodophor preparations may be better for skin disinfection in surgical settings. Povidone-iodine and iodine povacrylex show comparable results, and both achieve better reduction of surface pathogens than chlorhexidine. However, further study is needed before recommending one solution over another. Surgeons should consider the patient risk factors for SSI and the planned surgical wound class when selecting an optimal preoperative skin preparation agent.
It should be noted that although chlorhexidine was inferior to povidone-iodine in this particular trial, this does not mean it is inferior in all disinfection protocols (like preventing bacterial contamination of apheresis platelets). Chlorhexidine remains a well-established skin preparation method, and we need to evaluate it objectively.
Click to View: Mantacc Preoperative Swabs
Reference
Swenson BR, Hedrick TL, Metzger R, Bonatti H, Pruett TL, Sawyer RG. Effects of preoperative skin preparation on postoperative wound infection rates: a prospective study of 3 skin preparation protocols. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009 Oct;30(10):964-71. doi: 10.1086/605926. PMID: 19732018; PMCID: PMC3371364.