News and Blogs
How Effectively Can Environmental Sampling of Trees Detect Mammals?
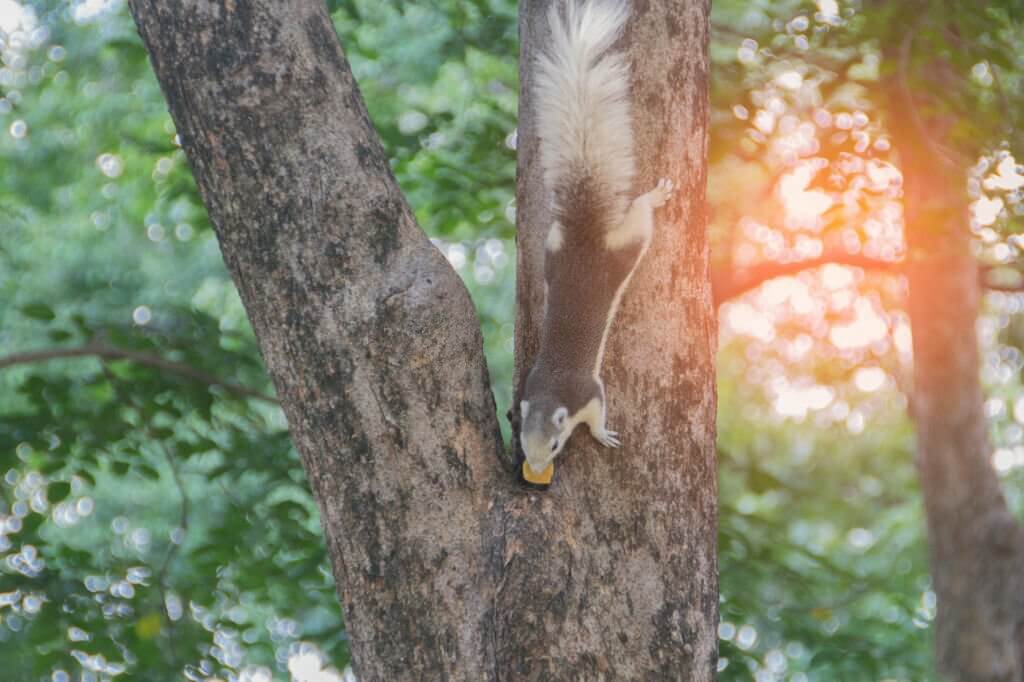

New DNA-based techniques offer the potential to revolutionize how scientists monitor mammal populations and distributions. Instead of relying on observation, trapping, or camera footage, environmental DNA (eDNA) methods detect genetic material shed into the local environment. A study in 2023 tested using eDNA collected from trees and surrounding soil to survey cryptic, arboreal (tree-dwelling) mammals.
Can We Find Mammals by Sampling Tree Bark and Soil?
Scientists tested new methods to survey mammals using DNA collected from the environment, known as environmental DNA or eDNA, instead of seeing or trapping animals directly. They wanted to know if eDNA could effectively detect arboreal (tree-dwelling) mammal species, which are often hard to monitor.
What Did They Sample and Where?
The researchers sampled the bark of tree trunks and soil around the base of trees in two New Jersey, USA forests, expecting to find DNA from bats, squirrels, and other mammals living in the trees. They sampled 21 trees total, collecting bark samples by rolling a damp paint roller up tree trunks to collect any residual DNA.
What Species Did They Detect?
DNA sequencing revealed the presence of 16 mammal species from the samples, including 8 arboreal species. Over 60% of the mammal diversity known to occur in the forests was detected. Tree bark samples revealed more species and DNA overall than soil samples. But both methods produced fairly similar mammal communities.
How Well Did eDNA Detect Bats and Squirrels?
Squirrel DNA was readily detectable on tree bark and in soil. However, most bat species expected to be present were missed, likely due to challenges detecting bat DNA with the DNA sequencing methods used. Adding additional DNA detection steps for specific bat species may improve detection.
Could eDNA Replace Trapping Mammals?
While more research is needed to optimize DNA methods, the study shows promise for environmental DNA as an easier alternative to setting traps or cameras to survey cryptic mammals living in forests and trees. Repeatedly sampling bark DNA could be especially useful for monitoring and conserving threatened arboreal mammals globally.
Click to View → Mantacc ST-25 PBS Environmental Sampling Kit
References
Allen MC, Kwait R, Vastano A, Kisurin A, Zoccolo I, Jaffe BD, Angle JC, Maslo B, Lockwood JL. Sampling environmental DNA from trees and soil to detect cryptic arboreal mammals. Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 5;13(1):180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27512-8. PMID: 36604526; PMCID: PMC9814459.
Related Posts
How Does Environmental Sampling Aid Zoonotic Disease Surveillance?
Factors Influencing Environmental Sampling You Need To Know
Environmental Sampling in Egg Safety Programs for Cage-Free Systems