Where Do Oropharyngeal Swabs Fit in TB Diagnosis?
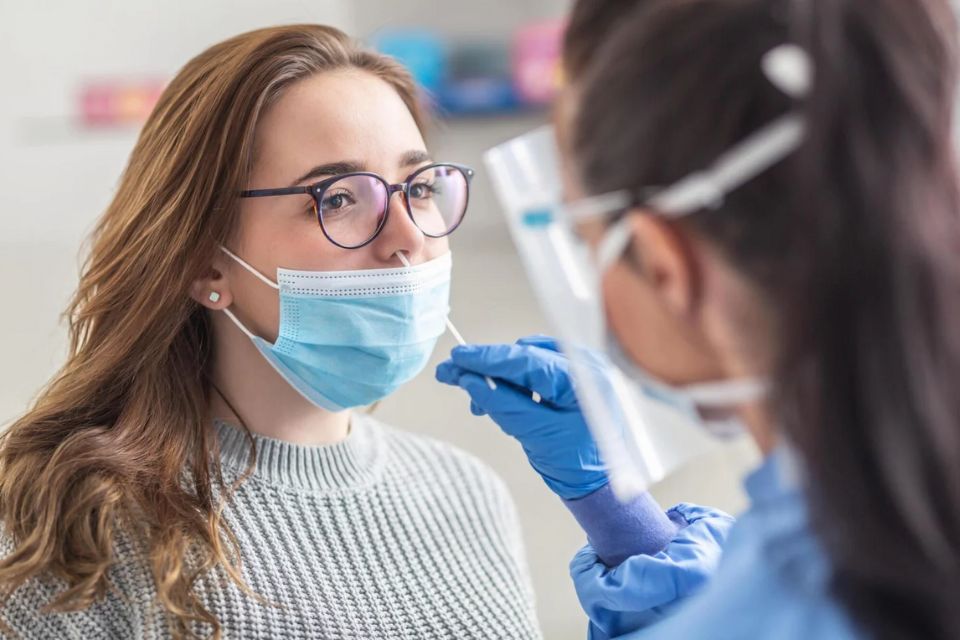
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global health challenge, with millions of new cases reported annually. Diagnosing TB, especially in certain populations, can be challenging due to the difficulty in obtaining sputum samples. This is where oropharyngeal swabs come into play, offering a promising alternative for TB detection.
Why Oropharyngeal Swabs?
Oropharyngeal swabs offer a non-invasive and patient-friendly approach to TB diagnosis. Unlike traditional sputum collection methods, swabbing the oral cavity is a simple and painless procedure, making it more accessible and convenient for patients.
How Effective Are Oropharyngeal Swabs?
The accuracy of oropharyngeal swabs in detecting TB has been extensively studied. According to the systematic review, sensitivity rates ranging from 36% to 91% have been reported in adults, with specificity generally exceeding 90%. While sensitivity in children is lower (5% to 42%), further optimization of sampling and processing methods could enhance its performance.
Factors Influencing Accuracy
Several factors contribute to the variability in sensitivity and specificity observed across studies. These include the type of swab used, the anatomical site swabbed (e.g., tongue, buccal mucosa), the molecular diagnostic test employed, and the sample processing methods. Optimizing these variables could lead to improved accuracy.
The Tongue Swab Advantage
Interestingly, swabbing the tongue appears to yield higher sensitivity compared to other oral cavity sites. Studies have reported sensitivity rates of up to 91% when using tongue swabs in adults. This finding highlights the potential benefits of focusing on tongue sampling for future research and clinical applications.
Accommodating Diverse Populations
One of the significant advantages of oropharyngeal swabs is their potential to improve TB diagnosis in populations that struggle with sputum production, such as children and individuals living with HIV. By offering a non-invasive alternative, these swabs could enhance access to accurate TB testing for vulnerable groups.
Compatibility with Existing Diagnostics
Recent studies have demonstrated that oropharyngeal swabs can be successfully used with established molecular diagnostics like the Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay. This compatibility with existing platforms could facilitate the integration of oropharyngeal swabs into routine TB testing workflows.
The Path Forward
While the current research highlights the potential of oropharyngeal swabs, further optimization and standardization of sampling and processing methods are needed. Establishing a consensus protocol for swab collection, transport, storage, and analysis would facilitate accurate comparisons across studies and contribute to the development of a robust diagnostic tool.
Therefore…
Oropharyngeal swabs represent a promising advancement in TB diagnosis, offering a non-invasive, patient-friendly approach with the potential for high accuracy. By addressing the limitations of traditional sputum-based testing, these swabs could revolutionize TB detection, particularly in populations where obtaining sputum samples is challenging. With continued research and optimization, oropharyngeal swabs may become a game-changer in the fight against this global health threat.
Click to View → Mantacc 93050C Oropharyngeal Swabs
References
Oral swabs with a rapid molecular diagnostic test for pulmonary tuberculosis in adults and children: a systematic review